Colchicine
Colchicine
- In our pharmacy, you can buy colchicine without a prescription, with delivery in 5–14 days throughout Australia. Discreet and anonymous packaging.
- Colchicine is used for the treatment of gout (acute attacks and prevention) and familial Mediterranean fever. It works by inhibiting inflammation and affecting the migration of white blood cells.
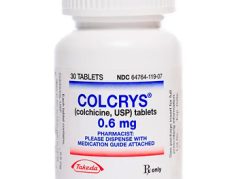
- The usual dosage for acute gout flare is 1.2 mg initially, followed by 0.6 mg one hour later; for prevention, it is 0.6 mg once or twice daily.
- The form of administration is a tablet.
- The effect of the medication begins within a few hours.
- The duration of action is approximately 1-3 days.
- Do not consume alcohol.
- The most common side effect is diarrhea.
- Would you like to try colchicine without a prescription?
Basic Colchicine Information
- INN (International Nonproprietary Name): Colchicine
- Brand names available in Australia: Colgout, Colchicine Juno
- ATC Code: M04AC01
- Forms & dosages: Tablets 0.5 mg
- Manufacturers in Australia: Arrow Pharma, Juno
- Registration status in Australia: Prescription only
- OTC / Rx classification: Prescription medication (Rx)
Everyday Use & Best Practices
Taking colchicine as part of your daily routine can have a profound impact on managing conditions such as gout. Understanding the optimum times to incorporate this medication aligns with Australian daily habits. Many patients find success with their dosing routines by considering their lifestyle.
Morning Vs Evening Dosing (Australian Daily Routines)
Choosing the right time to take colchicine often rests on your daily rhythm. Here are some tips to optimise your dosing:
- Morning doses may suit those who start their day early, allowing time for the medication to take effect.
- If you have a busy day ahead, consider taking your medication in the evening to prevent any potential side effects from interfering with your daytime activities.
- Align your dosing with other medications for convenience, especially if you take anti-inflammatory drugs alongside.
Taking With Or Without Meals
The way food interacts with colchicine is crucial. When consumed with a meal, colchicine's absorption may be affected. Here are some practical considerations:
- Empty stomach doses tend to enhance absorption, so consider taking your dose at least 30 minutes before eating.
- If you experience gastrointestinal distress, taking it with food might alleviate some discomfort.
- Given Australia's diverse culinary landscape, plan your meals to accommodate the timing of your medication.
Safety Priorities
Safety is paramount when initiating treatment with colchicine. Certain individuals should exercise caution or avoid this medication entirely. A good understanding of who should steer clear can prevent adverse outcomes.
Who Should Avoid It (TGA Safety Notices)
Patients in the following categories should avoid using colchicine:
- Those with severe kidney or liver issues.
- Individuals with known hypersensitivity to colchicine or any of its components.
- Patients currently on strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Activities To Limit (Driving, Machinery, Workplace Safety)
Colchicine side effects may impact daily activities, so consider scheduling these accordingly:
- Plan to limit driving or operating heavy machinery until you're aware of how colchicine affects you.
- Choose times for medication that do not coincide with critical work tasks that demand full alertness.
Dosage & Adjustments
Understanding how to properly dose colchicine according to Australian guidelines ensures effective treatment. The Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) provides clear prescribing information to help patients manage their dosages.
General Regimen (PBS-Listed Guidelines)
For adults, the standard dosing regimen is as follows:
- Initial treatment of acute gout: 1.2 mg at the first sign of a flare, followed by 0.6 mg one hour later.
- For prevention, a maintenance dose of 0.6 mg once or twice daily is advised.
Special Cases (Elderly, Indigenous Health, Comorbidities)
Certain populations require specific attention when prescribing colchicine:
- The elderly may necessitate a reduced initial dose due to varying renal function.
- Indigenous patients could have differing responses; thus, individual assessment is vital.
- Patients with comorbid conditions, like kidney problems, may need tailored dosing adjustments to enhance safety.
User Testimonials
Feedback from users is an invaluable part of understanding how colchicine positively impacts quality of life.
Positive Reports From Australian Patients
Many Australians have shared successful experiences with colchicine:
- Users have noted effective pain relief during gout flare-ups.
- Improvement in mobility and a return to daily activities are common.
Common Challenges (Forums, ProductReview Insights)
While many appreciate the benefits, some challenges arise:
- Gastrointestinal side effects like diarrhea are frequently reported.
- Patients express concerns about the timing and drug interactions with ibuprofen or allopurinol.
Buying Guide
Purchasing colchicine in Australia is straightforward. Here’s where to look:
Pharmacy Sources (Chemist Warehouse, Priceline, TerryWhite Chemmart)
Common pharmacies where colchicine can be purchased include:
- Chemist Warehouse
- Priceline
- TerryWhite Chemmart
Having a discussion with pharmacists can provide additional guidance and support regarding the medication's use.
Price Comparison (PBS Vs Private)
Costs may vary between public and private prescriptions. Below is a simplified comparison:
| Type | Cost (AUD) |
|---|---|
| PBS Prescribed | ~$6.80 |
| Private Purchase | ~$20.00 |
This information facilitates informed decision-making for patients considering their options.
What’s Inside & How It Works
Ingredients overview
Colchicine products available in Australia, specifically Colgout and Colchicine Juno, contain the active ingredient colchicine. Examining their composition provides clarity on what users are consuming.
| Brand Name | Active Ingredient | Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Colgout | Colchicine | 0.5 mg |
| Colchicine Juno | Colchicine | 0.5 mg |
Mechanism basics explained simply
Colchicine works primarily by inhibiting inflammation associated with gout attacks. When there's an increase in uric acid levels, sharp crystals can form and trigger painful inflammations in joints. Colchicine interferes with processes that lead to this inflammation, ensuring that pain and swelling are reduced. Think of it as a calming agent that soothes the irritation, allowing individuals to regain comfort.
Main Indications
Approved uses under TGA
The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) in Australia has approved colchicine for several medical conditions. Here's a quick overview of what it's used for:
- Acute gout flares
- Chronic gout prevention
- Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF)
- Pericarditis (off-label)
Off-label uses in Australian clinics
Beyond its approved uses, colchicine finds application in treating various conditions in Australian clinics. Some practitioners prescribe it to manage chronic pain associated with conditions such as cardiovascular diseases and inflammation disorders. Anecdotal evidence supports its effectiveness as part of a multi-drug regimen. Recent studies hint at positive impacts on heart health, stirring interest among researchers and healthcare providers alike.
Interaction Warnings
Food interactions (alcohol, coffee, Australian diet context)
Colchicine may interact unfavourably with certain foods and beverages found in the typical Australian diet. Alcohol can increase the risk of side effects, particularly gastrointestinal issues. Coffee and other caffeinated beverages may amplify these effects. Opting for non-alcoholic beverages and reducing caffeine intake during treatment could ease potential discomfort.
Drug conflicts tracked by TGA & PBS
Managing drug interactions is crucial for safety. Here’s a checklist of medications that may interact with colchicine:
- Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, erythromycin)
- P-glycoprotein inhibitors (e.g., cyclosporine)
- Other medications metabolised through similar pathways
Healthcare providers should be consulted to adjust dosages accordingly and avoid combinations that could lead to toxicity.
Latest Evidence & Insights
Major Australian and international studies 2022–2025
Recent studies have shone light on the effectiveness and safety of colchicine. Research published in top Australian medical journals has reported on its promising role in managing gout flare-ups and providing relief for patients suffering from FMF. International conferences have echoed similar findings, making colchicine a pivotal topic of discussion among healthcare professionals seeking innovative ways to treat inflammatory conditions.
Alternative Choices
Comparable PBS-listed medicines with pros/cons checklist
If colchicine does not suit an individual’s needs, there are alternatives to consider. Some comparable PBS-listed medicines include:
| Medication | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Allopurinol | Prevents uric acid formation | May cause skin rashes |
| Febuxostat | Effective at lowering uric acid | Potential liver function concerns |
| Probenecid | Enhances uric acid excretion | Not suitable for all patients |
Each alternative has its benefits and potential drawbacks. It's vital for individuals to discuss these options with their healthcare provider for personalised treatment plans.
Regulation Snapshot
In Australia, colchicine is regulated as a prescription-only medication by the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). It is primarily used for the management of acute gout flares, the prevention of gout attacks, and for certain cases of Familial Mediterranean Fever. The stringent guidelines ensure that colchicine is only prescribed when necessary, which is crucial considering its potential side effects and interactions.
The Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) plays a significant role in influencing pricing and accessibility. When a medication like colchicine is subsidised under the PBS, it dramatically reduces the out-of-pocket cost for patients. This allows broader access for those who might otherwise find the cost prohibitive. The subsidy framework ensures that patients can obtain colchicine at a nominal fee, making it a more viable treatment option for those affected by conditions like gout.
The combination of TGA regulations and PBS subsidies ensures responsible use while enhancing affordability, ultimately improving patient outcomes in Australia.
FAQ Section
Can I take colchicine with allopurinol?
Yes, colchicine and allopurinol can be taken together as part of a gout management plan, but it is best to consult a healthcare provider for the appropriate regimen.
What are the side effects of colchicine?
Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain. Severe side effects can involve multi-organ failure in cases of overdose.
How should I take colchicine for acute gout?
The typical initial dosage is 1.2 mg taken at the first sign of a flare, followed by an additional 0.6 mg one hour later.
Is colchicine available over the counter in Australia?
Colchicine is not available over the counter; it requires a prescription, although it can be relatively easy to obtain from a pharmacy.
Guidelines for Proper Use
Australian pharmacist counselling style
Pharmacists typically provide essential advice when patients begin their colchicine regimen. This includes:
- Understanding the importance of adhering to the prescribed dosage to prevent toxicity.
- Discussing the potential side effects, particularly gastrointestinal ones, and encouraging patients to report any adverse symptoms immediately.
- Advising on the necessity of regular follow-ups to monitor the effectiveness and safety of the treatment.
Advice from PBS and national health authorities
Health authorities recommend that patients using colchicine should be educated about:
- The correct dosage and maximum limits to avoid overdose.
- The importance of lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes, to manage gout effectively.
- Checking for possible drug interactions, particularly with stronger medications such as those affecting the liver.
These guidelines and recommendations aim to optimise patient safety and treatment effectiveness while reducing the risk of complications associated with colchicine use.
Delivery Information
| City | Region | Delivery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Sydney | New South Wales | 5–7 days |
| Melbourne | Victoria | 5–7 days |
| Brisbane | Queensland | 5–7 days |
| Perth | Western Australia | 5–7 days |
| Adelaide | South Australia | 5–7 days |
| Hobart | Tasmania | 5–9 days |
| Canberra | Australian Capital Territory | 5–7 days |
| Gold Coast | Queensland | 5–7 days |
| Newcastle | New South Wales | 5–9 days |
| Central Coast | New South Wales | 5–9 days |
| Cairns | Queensland | 5–9 days |
| Wollongong | New South Wales | 5–9 days |
| Sunshine Coast | Queensland | 5–9 days |
| Geelong | Victoria | 5–9 days |