Harvoni
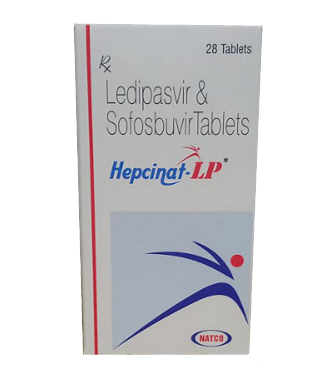
Harvoni
- In our pharmacy, you can buy Harvoni without a prescription, with delivery available throughout Australia. Discreet and anonymous packaging.
- Harvoni is used for the treatment of hepatitis C, featuring a combination of ledipasvir and sofosbuvir which disrupt viral processes by inhibiting specific enzymes.
- The usual dosage of Harvoni for adults with HCV genotype 1 is 1 tablet (90 mg/400 mg) daily for 8-12 weeks, while other genotypes have specified regimens.
- The form of administration is a tablet or oral pellets.
- The effect of the medication starts within a few days, but may take a couple of weeks for full viral suppression.
- The duration of action can last throughout the treatment period, generally 24 hours in the body.
- It is advised to avoid alcohol while on this medication.
- The most common side effects include headache, fatigue, nausea, and diarrhea.
- Would you like to try Harvoni without a prescription?
Basic Harvoni Information
• International Nonproprietary Name (INN): Ledipasvir and Sofosbuvir
• Brand names available in Australia: Harvoni
• ATC Code: J05AP51
• Forms & dosages: Tablets available as 90 mg ledipasvir/400 mg sofosbuvir
• Manufacturers in Australia: Gilead Sciences Inc., Asegua Therapeutics LLC.
• Registration status in Australia: Prescription only
• OTC / Rx classification: Rx only
Morning Vs Evening Dosing (Australian Daily Routines)
Finding a convenient time to take Harvoni is vital for adherence, especially considering how it fits into daily life in Australia. Many individuals opt for a once-daily dosage as per physician recommendations, making it crucial to decide on either morning or evening dosing that resonates with personal routines.
Adhering to a flexible schedule is important. For some, mornings might be the best option, aligning with other daily habits. Others might prefer taking it in the evening, allowing for a quieter period without interruptions. Ergonomics of daily life can enhance medication compliance. Factors such as work shifts, family obligations, or social activities should all be considered.
It's worth noting that dosing time may affect absorption. For effective management of Hepatitis C, inconsistency can lead to fluctuating drug levels in the body. Thus, sticking to a specific time every day is advised. This helps maintain stable blood concentrations of the medication, thus maximising its efficacy.
Taking With Or Without Meals
When it comes to taking Harvoni, the good news is that it can be taken with or without food. Flexibility in meal timing and medication can be quite beneficial. However, taking the drug with food may not only ease digestive comfort but can also improve the absorption of active components.
In an Australian context, traditional meal habits, which often include substantial breakfasts or breakfasts comprising lighter options, can seamlessly incorporate Harvoni. A hearty meal may enhance the uptake of the medication. Supermarket staples like bread, eggs, and fruits blend well with the timing of the medication.
While there are no strict dietary restrictions associated with Harvoni, it’s wise to be cautious with certain foods. For instance, heavy, fatty meals might delay gastric emptying, possibly influencing how well the drug is absorbed. Remaining mindful of alcohol consumption is also important; while moderate drinking may not specifically interfere with Harvoni, excessive consumption can lead to liver complications, which are counterproductive to treatment.
In conclusion, choosing a consistent time to take Harvoni and taking it with or without meals depends largely on personal preferences and daily routines. Finding a balance can significantly improve adherence and overall treatment success.
Safety Priorities
Using Harvoni for treating hepatitis C can be a game changer, but it’s essential to prioritise safety. While many patients can benefit from this antiviral medication, specific safety guidelines must be acknowledged. For individuals on Harvoni, it’s crucial to be informed about who should avoid it, potential side effects, and any restrictions related to activities like driving or operating heavy machinery.
The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) in Australia offers essential guidelines that everyone should consider before starting treatment. With the right information, patients can ensure a safer journey toward recovery, fully aware of potential risks and precautions.
Who Should Avoid It (TGA Safety Notices)
The TGA has outlined clear categories of individuals who are advised against using Harvoni:
- Hypersensitivity: Individuals with known allergic reactions to ledipasvir or sofosbuvir should steer clear of Harvoni.
- Severe liver conditions: Those suffering from severe hepatic impairment or decompensated cirrhosis need to avoid this medication unless under close supervision from a specialist.
- Strong drug interactions: Certain medications, particularly strong P-gp inducers like rifampin or St. John’s wort, may hinder Harvoni's effectiveness and should not be taken concurrently.
- Severe bradycardia: Caution is recommended for those using amiodarone, as it may intensify heart issues when combined with Harvoni.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals: Safety has not been established, so these groups should consider alternatives unless the benefits significantly outweigh the potential risks.
Activities to Limit (Driving, Machinery, Workplace Safety)
Patients on Harvoni often wonder about the impact of treatment on daily activities, particularly driving or operating heavy machinery. While Harvoni is generally well tolerated, some side effects may impair coordination and alertness.
Common side effects include:
- Fatigue: This can significantly affect focus and energy levels.
- Headaches: Migraines or tension headaches may arise unexpectedly.
- Nausea: This can create discomfort, particularly during the early stages of treatment.
Given these factors, patients on Harvoni should exercise caution:
- Driving: If experiencing fatigue or drowsiness, it’s best to refrain from driving until feeling back to normal.
- Operating Heavy Machinery: Similar considerations apply as fatigue can impede reaction times and safety.
- Workplace Safety: Patients are encouraged to communicate openly with their employers about treatment side effects that could pose risks in the workplace.
In summary, while Harvoni can be an effective treatment for hepatitis C, it's crucial to heed the TGA's safety notices and approach daily activities with caution. Listening to one’s body and recognising when certain tasks might be too challenging can make a substantial difference. Keep communication lines open with healthcare providers for customised advice and ensure all treatment decisions prioritise safety first.
General Regimen (PBS-Listed Guidelines)
When it comes to treating hepatitis C, Harvoni is the go-to choice for many healthcare professionals. It's been approved for various patient groups, with specific dosages set out by the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) in Australia. Understanding these guidelines is crucial for ensuring an effective treatment regimen.
Here's a breakdown of standard dosages based on patient categories:
- For adults with HCV genotype 1: 1 tablet (90 mg ledipasvir/400 mg sofosbuvir) once daily for 8 to 12 weeks, which may extend to 24 weeks in complex cases like cirrhosis.
- Adults with genotypes 4, 5, or 6 typically take 1 tablet daily for 12 weeks.
- For children aged 3 years and above, weighing at least 35 kg: 1 tablet daily for 12 to 24 weeks based on their treatment history and cirrhosis status.
- Children under 35 kg are prescribed a weight-based dosage through oral pellets, also lasting between 12 to 24 weeks.
Regular monitoring during treatment is essential, especially for those on the longer regimens. Patients should be advised on what to do in case they miss a dose or experience side effects.
It’s also worth noting that while the standard doses are well-established, individual patient factors could lead to adjustments, particularly in the presence of comorbidities or complications.
Special Cases (Elderly, Indigenous Health, Comorbidities)
There are distinct considerations when treating specific populations, notably the elderly and Indigenous Australians. Not every treatment fits all, and some patient groups may require tailored approaches.
For the elderly, monitoring becomes crucial. Even though routine dosage adjustments aren’t generally necessary for Harvoni, age-related health changes can impact how the drug is metabolized:
- Regular liver function tests can be a good practice to monitor for any untoward effects.
- Close observation is essential for patients with various comorbidities, as multiple medications may interact.
Indigenous Australians often face unique health challenges. Adverse social determinants can lead to varying health outcomes, influencing both the effectiveness of the treatment and patient adherence. Important adjustments may include:
- Education on the medication and its benefits tailored to build trust.
- Access to healthcare facilities should be assessed to ensure proper follow-up.
- Consideration of mental health support is crucial for holistic care.
Finally, patients with comorbid conditions such as renal or hepatic impairment require extra diligence. Adjustments in treatment protocols will be necessary if:
- Patients have severe renal impairment where dosing may need modification, particularly with other concurrent therapies.
- Those with decompensated liver disease should only be treated under specialist care.
In essence, while Harvoni has a clear and effective regimen, the individuality of patients, particularly the elderly, Indigenous populations, and those with comorbidities, underlines the necessity for a tailored approach. Not a 'one-size-fits-all' scenario in hepatitis C management, but rather a continuum of care tailored to each patient’s needs.
Delivery Information
| City | Region | Delivery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Sydney | New South Wales | 5–7 days |
| Melbourne | Victoria | 5–7 days |
| Brisbane | Queensland | 5–7 days |
| Perth | Western Australia | 5–7 days |
| Adelaide | South Australia | 5–7 days |
| Hobart | Tasmania | 5–9 days |
| Canberra | Australian Capital Territory | 5–7 days |
| Newcastle | New South Wales | 5–9 days |
| Gold Coast | Queensland | 5–9 days |
| Wollongong | New South Wales | 5–9 days |
| Cairns | Queensland | 5–9 days |
| Dunedin | New Zealand | 5–9 days |
| Townsville | Queensland | 5–9 days |